Load balancing refers to efficiently distributing incoming network traffic across a group of backend servers, also known as a server farm or server pool.
Modern websites and applications generate lots of traffic and serve numerous client requests simultaneously.
Load balancing helps meet these requests and keeps the website and application response fast and reliable.
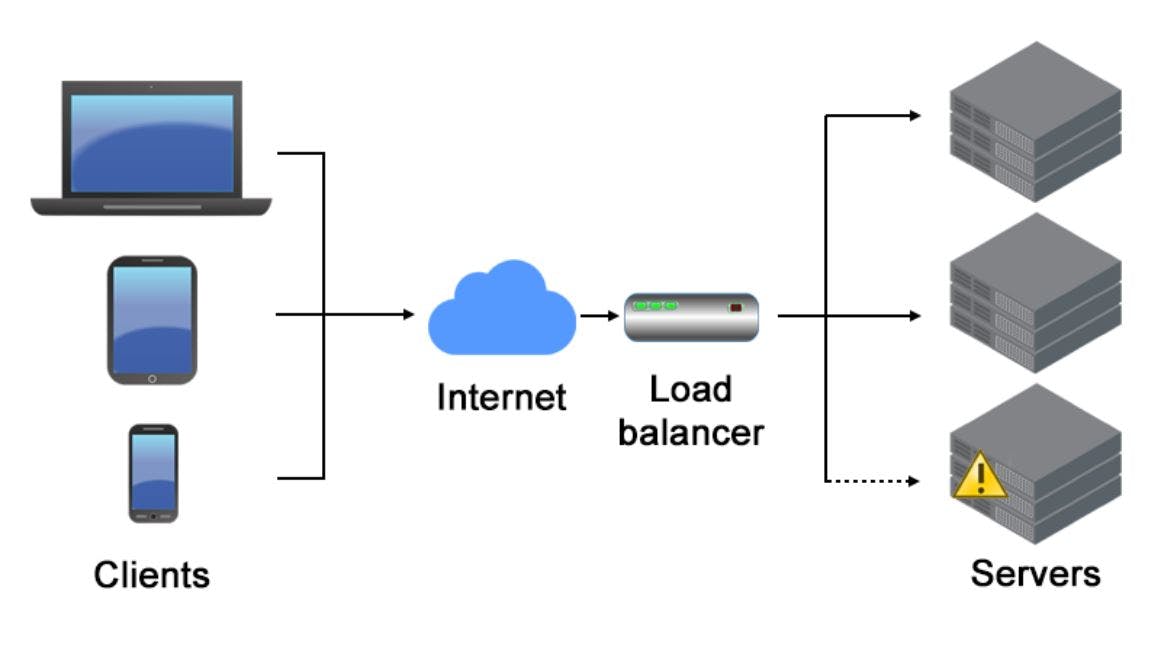
Load balancing performs these critical tasks:
- Manages traffic spikes and prevents spikes on a single server
- Minimizes user request response time
- Ensures performance and reliability of computing resources, both physical and virtual
- Adds redundancy and resilience to computing environments
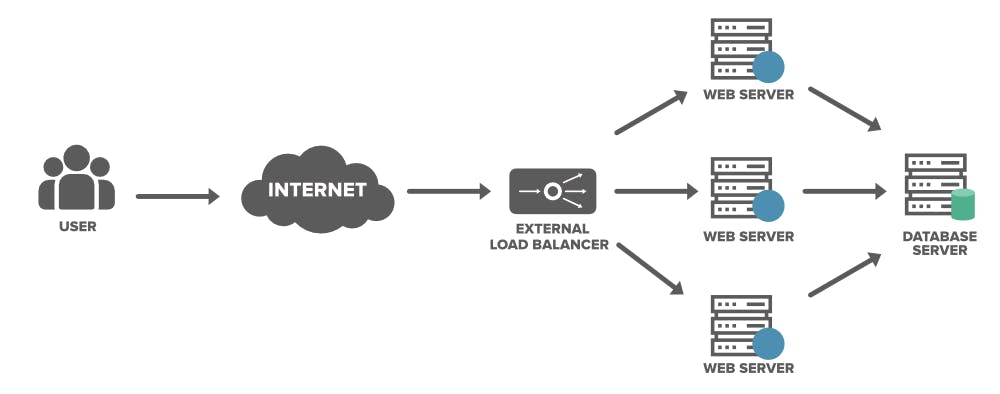
How does a Load Balancer works
- A client, such as an application or browser, receives a request and tries to connect with a server.
- A load balancer receives the request and based on the preset patterns of the algorithm, it routes the request to one of the servers in a server group (or farm).
- The server receives the connection request and responds to the client via the load balancer.
- The load balancer receives the response and matches the IP of the client with that of the selected server. It then forwards the packet with the response.
- Where applicable, the load balancer handles SSL offload, which is the process of decrypting data using the Security Socket Layer encryption protocol, so that servers don’t have to do it.
- The process repeats until the session is over.
Load Balancing Algorithms
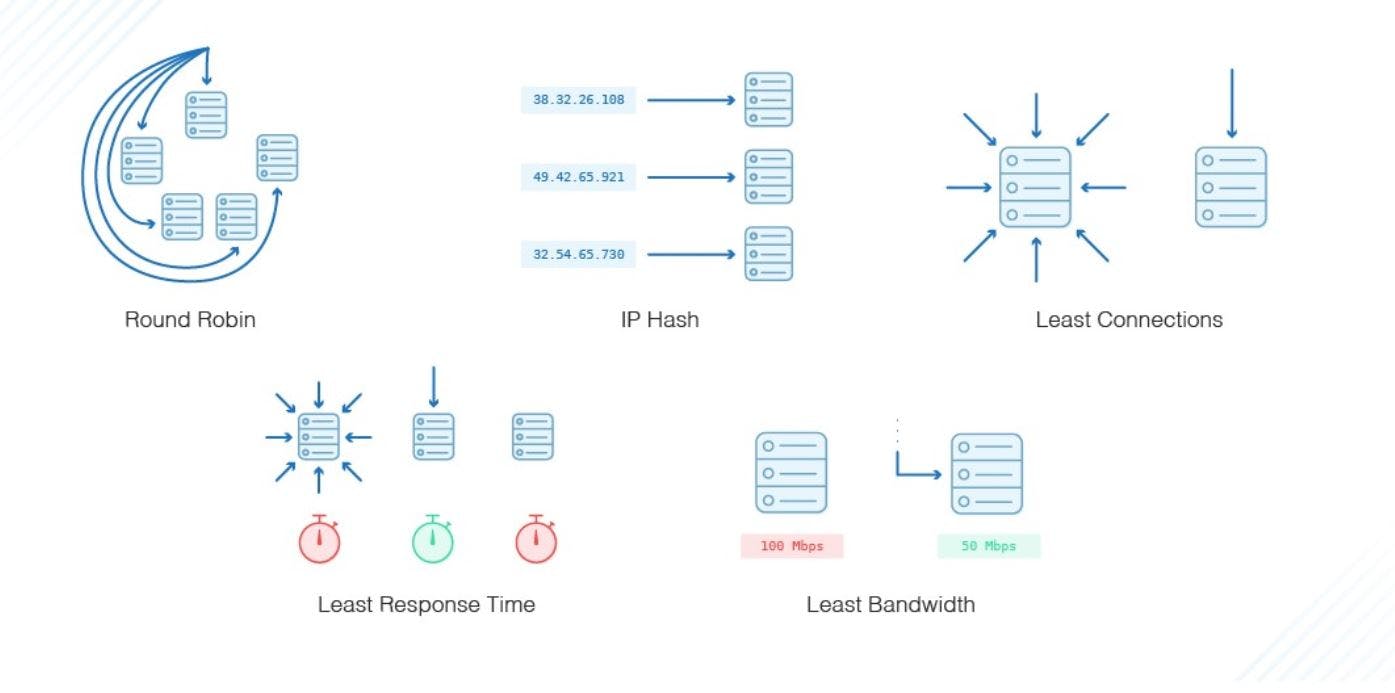
Different load balancing algorithms offer different benefits and complexity, depending on the use case. The most common load balancing algorithms are:
